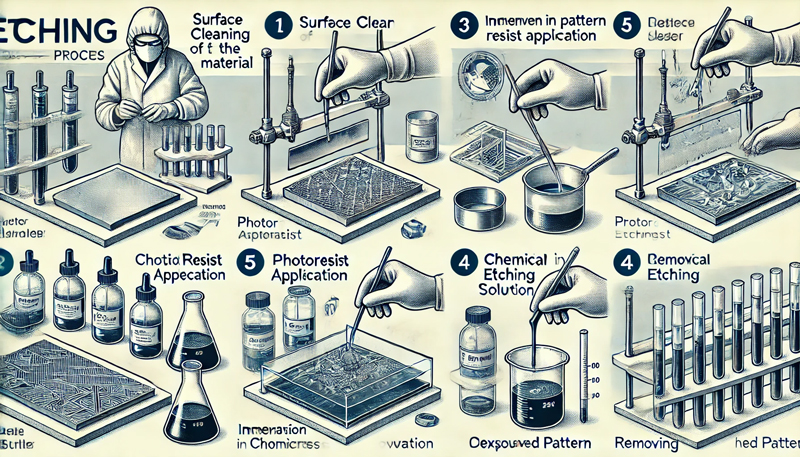
The chemical etching process is a process used to remove unwanted portions of a material's surface through a chemical reaction. It utilizes acids, bases, or other chemical solutions to dissolve the surface of a material, thereby etching a pattern or structure into the material. This process is widely used in metalworking, microelectronics, optics, aerospace and other fields.
The basic steps of the chemical etching process include the following:
Surface Cleaning: The surface of the material is first cleaned to remove oil, oxides and other impurities to ensure uniform etching.
Pattern design and photolithography: Using techniques such as photolithography or screen printing to form a protective layer on the surface of the material to protect areas that do not need to be etched. The protective layer is usually made with a photopolymer or resist.
Etching: The patterned material is immersed in a chemical etching solution, which dissolves only the exposed portion of the material, leaving the protected portion unaffected. The depth and speed of the etching process can be precisely adjusted by controlling the concentration, temperature and time of the solution.
Removal of Protective Layer: After the etching is completed, the protective layer is removed to obtain the desired pattern or structure on the surface of the material.
Acid etching solution: such as hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, used for etching copper, aluminum, stainless steel and other metals.
Alkaline etching solutions: such as sodium hydroxide, ammonia, used for etching some specific materials.
Oxidizer solutions: e.g. hydrogen peroxide for finer etching needs.
High precision: Suitable for creating detailed patterns at the micron or even nanometer level.
Low cost: particularly suitable for mass production.
Wide material compatibility: can handle a wide range of materials such as metal, glass, ceramics, etc.
The chemical etching process is widely used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards (PCBs), integrated circuits (ICs), precision filters, microfluidic chips, etc., and is able to meet the high demands for pattern complexity, precision and production efficiency.
Contact: andy_Lai
Phone: 18938693450
E-mail: yw9@zldsmt.com
Add: Building A3, Huafa Industrial Park, Fuyong Town, Fuyuan Road, Fuyong Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen,China